Mutual Funds and Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) are popular investment vehicles that offer investors a diversified portfolio of securities. In this blog we provide you with valuable information that can help you make informed decisions about your investment portfolio.

What are Mutual Funds?
Mutual Funds is an investment option that pools money from a number of investors who share a common investment objective and invests this money in stocks, bonds and other such securities. The pool of money is managed by a professional fund manager or a team of managers. These managers make investment decisions on behalf of the investors. The combined holdings, that is, the collection of securities, in the mutual funds is known as portfolio. The composition of the portfolio depends upon the fund’s investment objective and strategy.
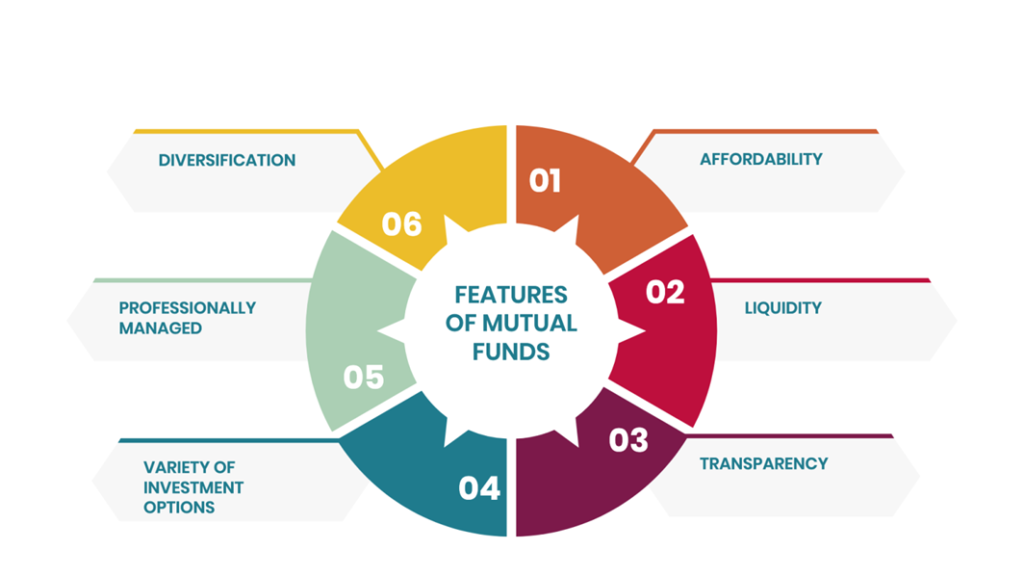
Features of Mutual Funds
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual Funds come in various types, each with its own objectives, strategies and risk profiles. Here are some of the different types of mutual funds.

1. Equity Funds- These funds invest primarily in stocks. They can be further categorized based on the type of stocks such as small-cap, mid-cap, large-cap, etc.
2. Bond Funds- They invest in bonds and other fixed income securities. Bond Funds focus on government bonds, corporate funds and municipal bonds.
3. Money Market Funds- They invest in bonds and other fixed income securities. Money Market Funds are considered low risk and it also provide stability to investors.
4. Hybrid Funds- They are also called Balanced Funds. They invest in a hybrid of asset classes like stocks, bonds and money market instruments. The objective of this fund is to reduce risk by exposure to different asset classes.
5. Sector Funds- They concentrate their investment to a particular sector or industry of the economy such as technology, health care, agriculture or energy.
What are Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)?

An Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) is a marketable security that tracks an index, a commodity, bonds, or a basket of assets like an index fund. Its trading value depends on the net annual value of the underlying stock it represents. It is a collection of investments such as equities or bonds. In simple it is an investment fund traded on stock exchange.
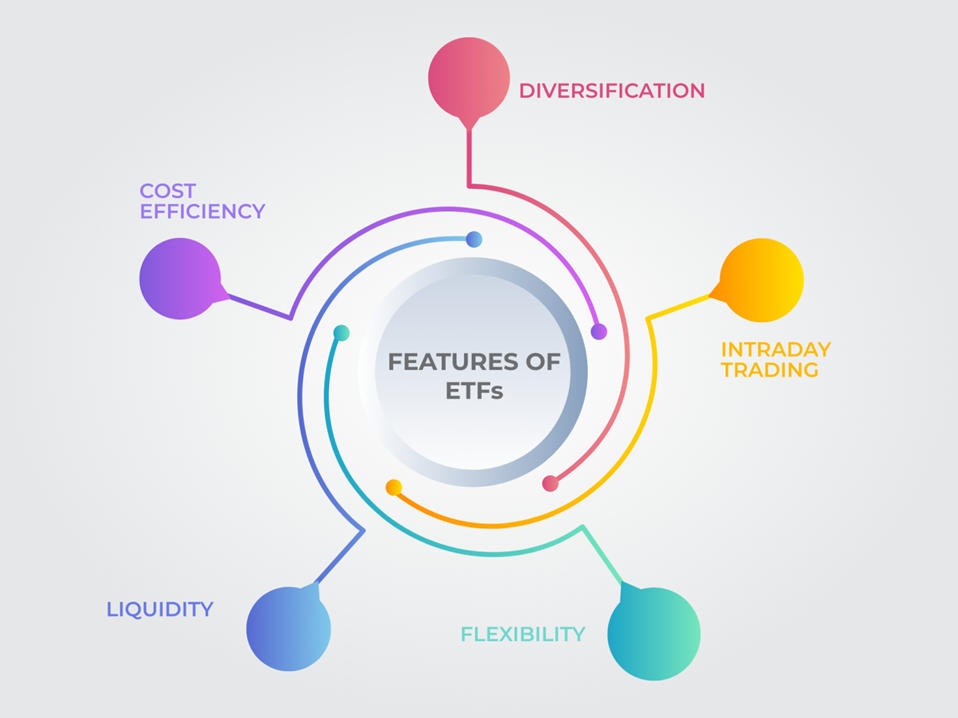
Features of ETFs
Types of Exchange Traded Funds
ETFs come in various types, each designed to meet different investment objectives and strategies. Given below are some of the different types of ETFs.
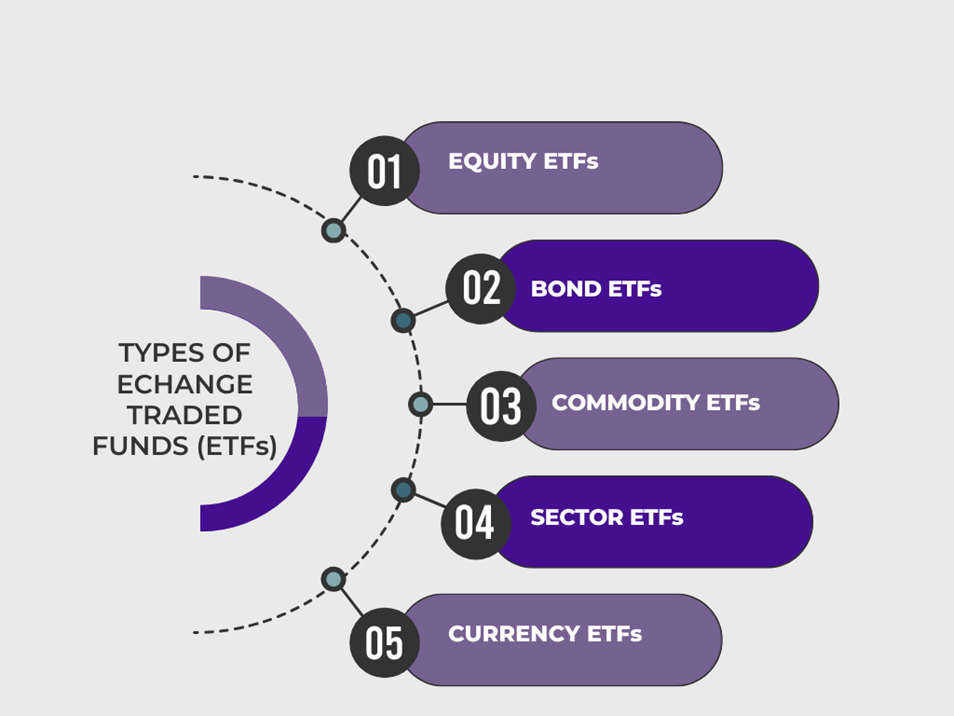
1. Equity ETFs- They invest primarily in stocks or equity securities. They may track a specific stock market index or focus on a particular sector, industry or region.
2. Bond ETFs- They invests in various fixed income instruments such as government bonds and debentures. Some fixed-income ETFs are categorized by the maturity of the bonds they hold. Example: short-term bond ETFs, intermediate-term bond ETFs, long-term bond ETFs, etc.
3. Commodity ETFs- They invest in physical commodities like gold, silver, oil, or agricultural products. They may hold the physical commodity itself or invest in futures contracts or other derivative instruments to track the price movements of the commodity.
4. Sector ETFs- They invest in companies within a specific sector of the economy such as technology, healthcare, energy or financial services. They allow investors to target specific industries or sectors that they believe will outperform the broader market.
5. Currency ETFs- They invest in foreign currencies or currency basket. They track the performance of a single currency or a group of currencies. Currency ETFs are used by investors to hedge currency risk or speculate on currency movements.
Difference Between Mutual Funds and ETFs
| MUTUAL FUNDS | EXCHNAGE TRADED FUNDS |
| Bought and sold through many channels | Bought and sold through broker-dealers |
| Not listed on stock exchanges | Listed on stock exchanges |
| Intraday trading is not possible | Intraday trading is possible |
| Most Mutual Funds maintain some cash in order to satisfy potential investor redemptions. | Generally, there is no cash needed |
| Priced on a daily basis at market close | Priced like an individual stock- constantly while the market is open |
Which one is better – Mutual Funds or ETFs?
ETFs can be traded throughout the day whereas mutual funds are traded at the end of the trading day at the fund’s net asset value (NAV). Mutual Funds have minimum investment requirements whereas ETFs does not have any minimum investment requirements. Ultimately, the decision between Mutual Funds and ETFs depends on various factors, including an investor’s individual preferences, investment goals, risk tolerance and the specific characteristics of each investment vehicle. It is best to consult a financial advisor who can assess your financial needs and can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Mutual Funds and Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) offer investors a diverse investment option to achieve their financial goals. Whether you choose Mutual Funds or ETFs, the key is to align your investment choice with your financial goals and risk tolerance. By understanding the two investment vehicles, you can build a portfolio that suits your needs and work towards financial success.
Example:
| SBI Nifty 50 ETF | Tracks the Nifty 50 Index, which consists of the 50 largest and most liquid stocks listed in National Stock Exchange. |
| HDFC S&P BSE Sensex ETF | Tracks the Sensex, which is composed of 30 large cap stocks representing various sectors of the Indian economy. |
| UTI Nifty Bank ETF Bees | Tracks the performance of the Nifty Bank Index, which comprises stocks of the banking sector, listed on National Exchange. |
| Nippon India ETF Gold | Tracks the price of gold and provide the investors an opportunity to invest in gold without owning physical gold. |
To know more about mutual funds click: BASICS OF MUTUAL FUNDS

